Product Name/Alternate Names: Inconel 825 wire, Alloy 825 wire
Material: Inconel 825 is a nickel-iron-chromium alloy with additions of molybdenum, copper, and titanium.
Color: Typically silver-gray
Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance in both oxidizing and reducing environments, good mechanical properties from cryogenic temperatures up to about 1000°C (1832°F).
Applications: Used in chemical processing, pollution control, oil and gas recovery, acid production, pickling operations, nuclear fuel reprocessing, and handling of radioactive wastes.
Principle: Its resistance to aqueous corrosion makes it suitable for various applications where resistance to corrosion and moderate mechanical properties are required.
Sizes: Available in various diameters ranging from small wires (e.g., 0.1 mm) to larger diameters used in industrial applications.
Use Differences of Products:
Applications:
Inconel 825 wire is used in various applications such as chemical processing, pollution control, and nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Divisibility:
It can be separated into three distinct products: wire for welding, wire for industrial heating elements, and wire for corrosion resistance.
Alternate Names:
Inconel 825 wire is also known by different names in the industry, including Alloy 825 wire and UNS N08825 wire.
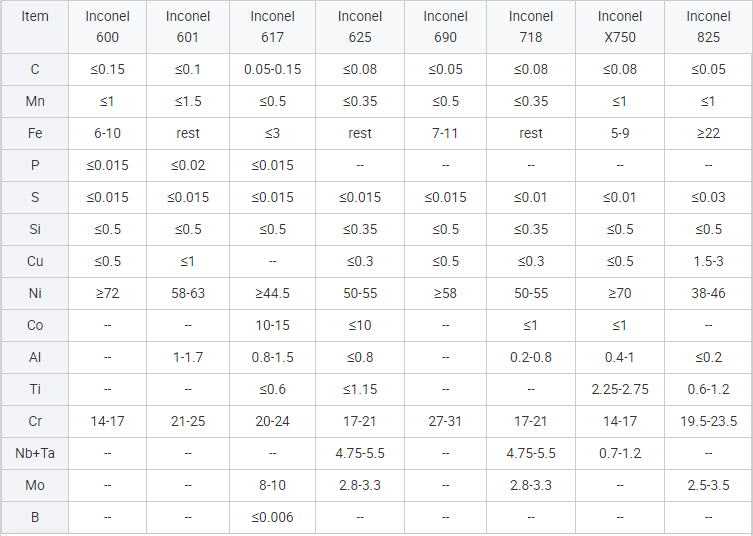

Product Features:
Corrosion Resistance: Inconel 825 wire is highly resistant to both reducing and oxidizing acids, stress corrosion cracking, and intergranular corrosion.
High Temperature Stability: It maintains its mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures up to 550°C (1022°F).
Weldability: It can be welded using conventional techniques, making it versatile for various applications.
Strength and Durability: Offers high strength properties suitable for demanding environments.
Chemical Processing: Used in equipment such as reactors, vessels, and pipelines for handling corrosive acids and alkalis.
Oil and Gas Industry: Valves, tubing, and components exposed to sour gas environments.
Marine Environments: Seawater desalination equipment, offshore platforms.
Nuclear Power: Used in reactor cores and auxiliary systems due to its resistance to radiation and high-temperature environments.
Technology and Principles:Inconel 825 wire is composed primarily of nickel, iron, and chromium, with additions of molybdenum, copper, and titanium. The alloy's resistance to corrosion stems from its stable austenitic structure and the formation of a passive oxide layer on its surface, enhancing its durability in aggressive chemical environments.
Applications:


Customed Service:

FAQ:
1. What is Inconel 825 wire?Inconel 825 wire is a nickel-iron-chromium alloy wire with additions of molybdenum, copper, and titanium. It is known for its excellent resistance to both reducing and oxidizing acids, stress-corrosion cracking, and localized attack such as pitting and crevice corrosion.
2. What are the typical applications of Inconel 825 wire?Inconel 825 wire is commonly used in various applications including chemical processing, pollution control equipment, oil and gas recovery, nuclear fuel reprocessing, acid production, and marine components.
3. What are the key properties of Inconel 825 wire?
High resistance to corrosion and oxidation
Good mechanical properties from cryogenic to moderately high temperatures
Excellent weldability and fabricability
Outstanding resistance to reducing and oxidizing acids
Good resistance to stress-corrosion cracking and localized attacks
4. What are the available forms of Inconel 825 wire?Inconel 825 wire is available in various forms including round wire, flat wire, and shaped wire. It can be supplied in coils, spools, or straight lengths depending on the application requirements.
5. How does Inconel 825 wire compare to other Inconel Alloys?Inconel 825 offers superior corrosion resistance compared to many other Inconel alloys, particularly in environments containing sulfuric and phosphoric acids. Its combination of chemical composition and heat treatment gives it unique properties suitable for harsh environments.
6. What are the welding considerations for Inconel 825 wire?Inconel 825 wire can be welded using conventional welding techniques such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and shielded metal arc welding (SMAW). Preheating and post-weld heat treatment are recommended to maintain the alloy's corrosion resistance properties.
7. Is Inconel 825 wire suitable for high-temperature applications?Yes, Inconel 825 wire maintains good mechanical properties at both cryogenic temperatures and moderately high temperatures (up to 1000°F or 540°C), making it suitable for applications in both extremes.
8. What industries commonly use Inconel 825 wire?Industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, marine environments, pollution control, and nuclear industries frequently utilize Inconel 825 wire due to its superior corrosion resistance and reliability in harsh conditions.
9. How is Inconel 825 wire typically supplied?Inconel 825 wire is supplied in various sizes and forms, ranging from thin wires for weaving and braiding to thicker wires for welding and structural applications. Suppliers offer customization options based on specific customer requirements.
10. What are the environmental considerations for using Inconel 825 wire?Inconel 825 wire is chosen for its resistance to aggressive environments, reducing the need for maintenance and replacement, thereby contributing to longer service life and reduced environmental impact.
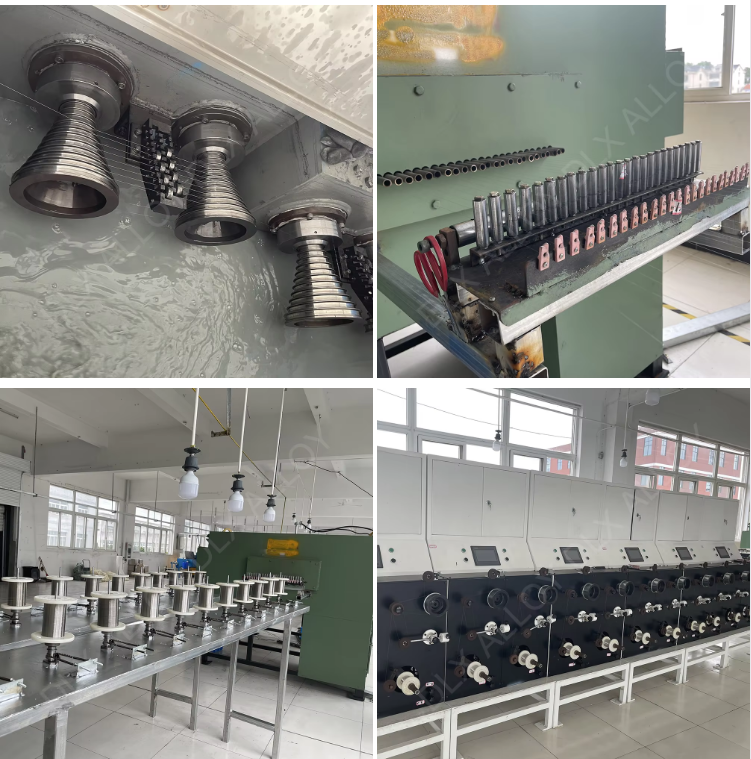
Production Process:
Raw Material Preparation:
Source high-quality Inconel 825 alloy.
Verify material certifications for composition and properties.
Wire Drawing:
Cold drawing process to reduce diameter.
Control temperature and speed to maintain material integrity.
Use lubricants to minimize friction and wear.
Annealing:
Heat treatment to relieve internal stresses.
Temperature and time controlled to achieve desired mechanical properties.
Prevent oxidation during annealing process.
Surface Treatment:
Pickling and passivation to remove scale and enhance corrosion resistance.
Mechanical polishing for specific surface finish requirements.
Quality Control:
Continuous monitoring of dimensions, mechanical properties, and surface quality.
Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing for defect detection.
Operating Methods:
Wire Handling:
Use clean, dry handling equipment to prevent contamination.
Avoid sharp bends or kinks that could cause stress concentrations.
Machining:
Use carbide tooling for cutting to minimize work hardening.
Coolant or lubricant application to manage heat generation.
Welding:
Preheat and post-weld heat treatment may be necessary.
Shielded gas welding techniques to prevent oxidation.
Precautions:
Corrosion Resistance:
Avoid exposure to environments with high chloride content.
Ensure proper surface preparation and maintenance.
Temperature Sensitivity:
Monitor operating temperatures to prevent embrittlement.
Control cooling rates after high-temperature processes.
Health and Safety:
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling chemicals or during welding operations.
Follow MSDS guidelines for safe handling of Inconel 825 alloy and associated chemicals.










